Gluten is a protein that has gained a bad reputation in the past few years. In addition, the plethora of medical information on the internet has blurred the clarity between coeliac disease and gluten intolerance.
Most people use these terms synonymously. However, symptoms, adversity, causes, duration, and conditions differ. This article clarifies the confusion and helps you understand which one you have.
Definition
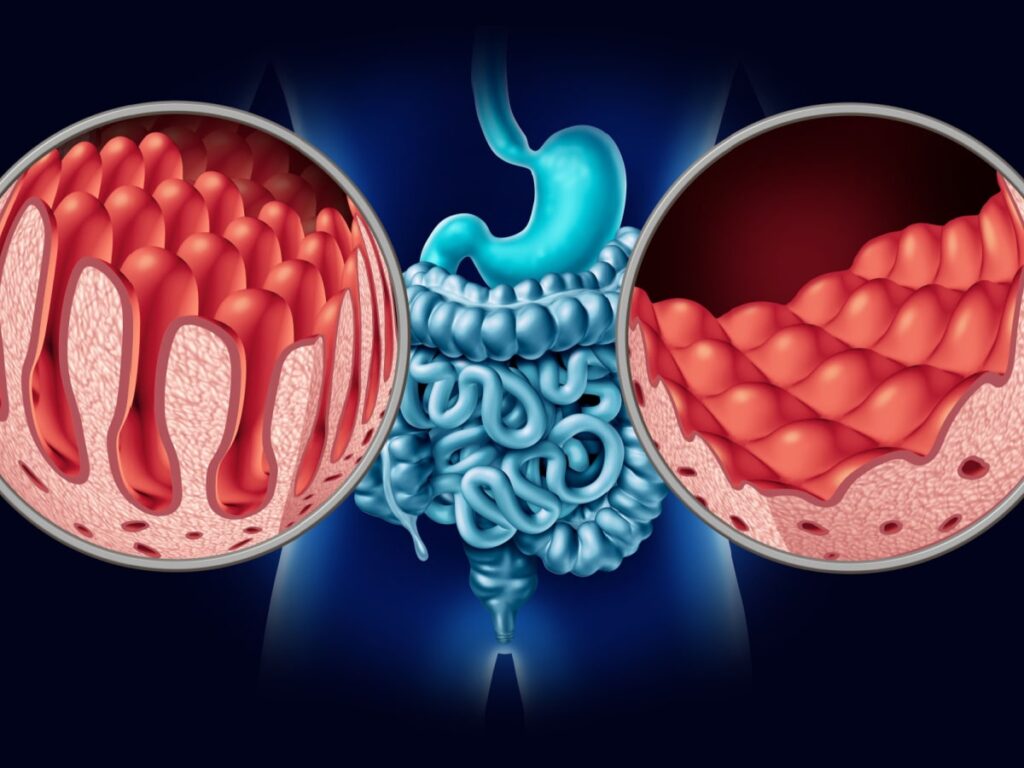
Coeliac Disease – The coeliac disease is an autoimmune digestive disorder in which food containing gluten causes an inflammatory response and damage to the lining (villi) of the small intestine. This lining of the small intestine is responsible for nutrient absorption. Hence, coeliac disease leads to poor gut health and malnutrition.
Gluten Intolerance – Gluten intolerance is a short-term adverse reaction to gluten foods. It doesn’t cause inflammatory responses like coeliac disease. There is no test for gluten intolerance. On the other hand, coeliac disease is only diagnosed through the coeliac test.
Symptoms
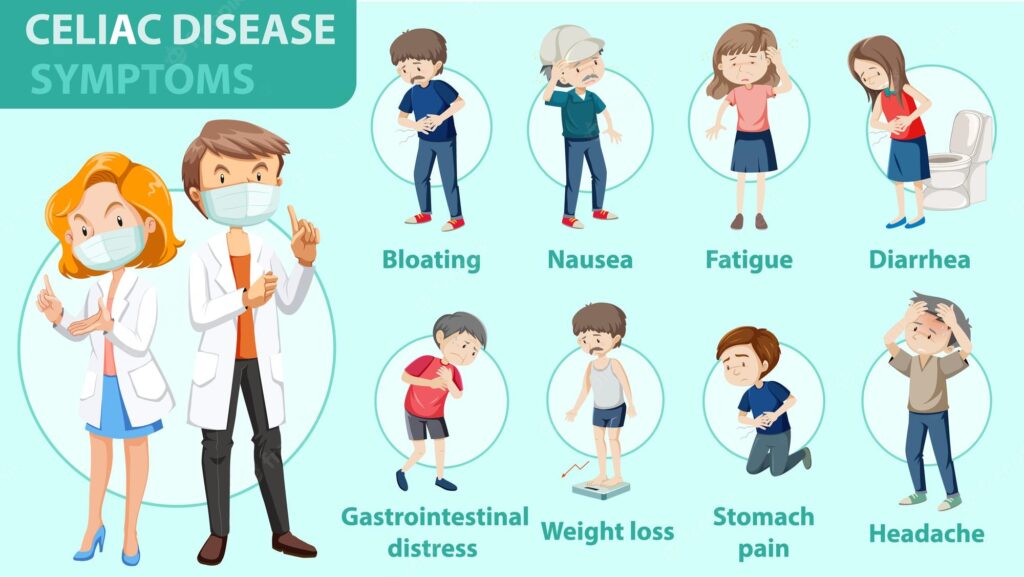
Coeliac Disease – The symptoms of coeliac disease and gluten intolerance may overlap. But here are some symptoms that indicate the diagnosis of coeliac disease;
- Skin blister or rash
- Vomit
- Malnutrition
- Delayed puberty
- Migraine
- Anaemia
- Fluctuating weight
The condition of coeliac disease is severe. If left untreated, it can lead to serious health concerns, such as;
- Infertility
- Cognitive impairment
- Cancer
- Osteoporosis
Gluten Intolerance – The symptoms of gluten intolerance are limited and can go away with multiple medication courses. Moreover, the symptoms of gluten intolerance are only limited to GI issues, including;
- Constipation.
- Fatigue.
- Haemorrhoids.
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
- Nausea.
- Anal fissures.
Tests
Coeliac Disease – Every coeliac test looks for the antibodies that are present in coeliac patients in your blood. Some common coeliac tests include;
- Blood Sample Test: It provides a comprehensive report along with the antibodies present in your blood.
- Skin Biopsy: It is another way for a coeliac test to include collecting a small tissue sample of your skin and examining it under the microscope.
- Skin Prick Test: This involves examining your skin reaction to gluten consumption.
- Intestinal Biopsy: It is a medical examination where a doctor inserts an endoscope from your mouth through the small intestine to collect a tissue sample and run it under a test.
Gluten Intolerance – To eliminate the possibility of coeliac disease, your doctor will first make sure to run the tests for coeliac disease.
If your report for coeliac disease is negative, you will be put on a temporary diet test. This diet includes gluten intake for a specific duration where the doctor assesses your body’s symptoms and reactions.
Treatment
Coeliac Disease – The treatment for the coeliac disease includes practising complete elimination from gluten foods. Your doctor may advise you to follow a medication plan of anti-inflammatory and multi-vitamin supplements if your disease worsens.
Gluten Intolerance – Gluten Intolerance can be easily managed. The symptoms of gluten intolerance are short-term and go away with proper prevention and care. You can lower the chances of gluten intolerance by following a gluten-free diet.
Final Words
If you are experiencing any health issues whenever you eat gluten-rich food, the first step you should take is to follow a gluten-free diet. And then, you should get yourself checked for gluten sensitivity or coeliac disease.
Gluten intolerance is manageable and has mild symptoms. In contrast, coeliac disease is long-term and demands consistent care and abstaining from a particular food.

